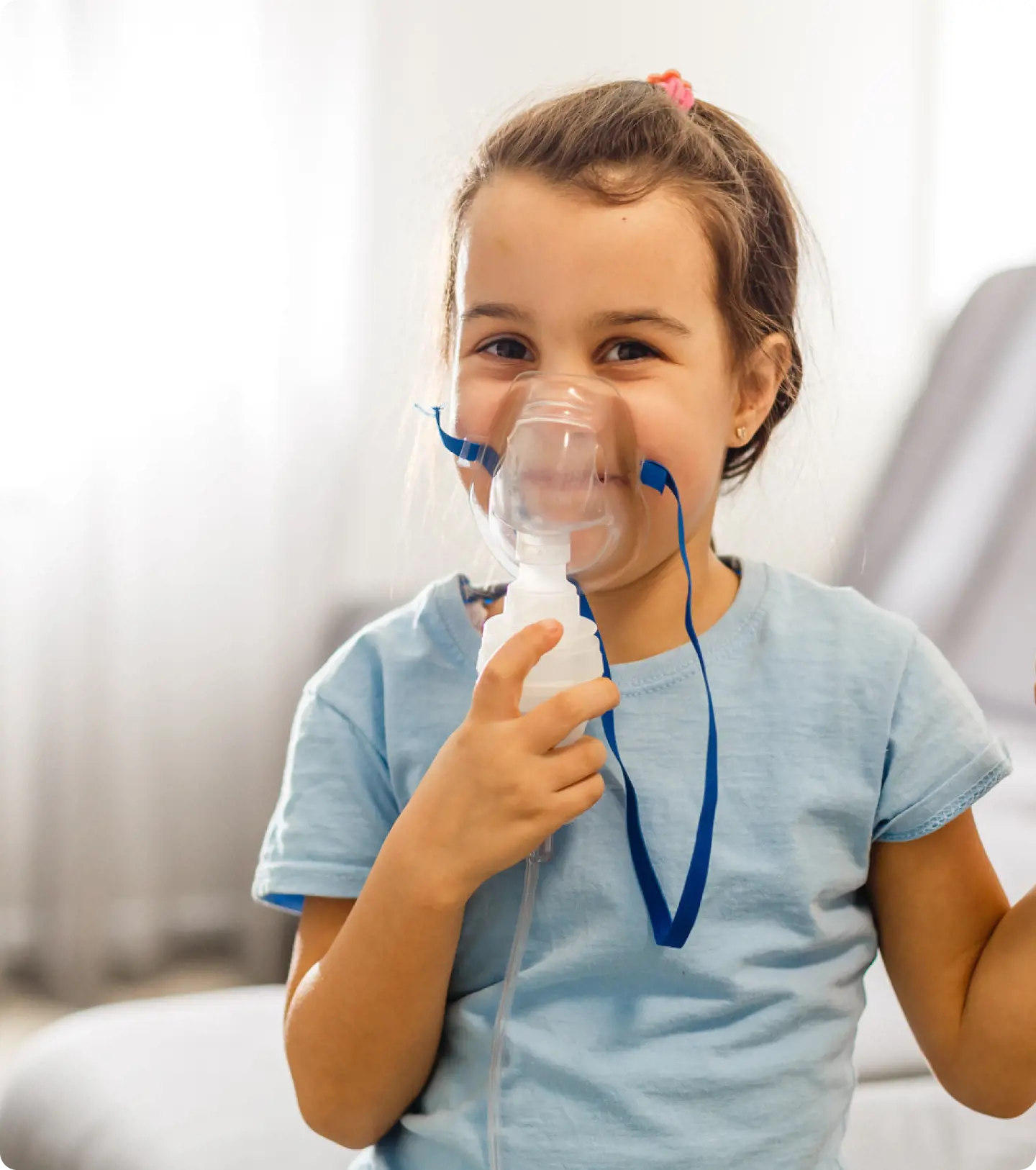
Nebulisers are devices for managing respiratory conditions like asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis. They deliver medicine directly to the lungs by turning liquid medication into a mist for easy inhalation.
While still used in specific cases, nebulisers are no longer the preferred method for asthma or COPD treatment. Spacers are equally effective, more convenient, and carry fewer side effects. Nebulisers remain useful for patients requiring oxygen supplementation, those unable to use inhalers, or with specific medical needs.
This guide explains what nebulisers are, how they work, when to use them, and tips for selection and maintenance.
What Is a Nebuliser?
A nebuliser is a medical device that transforms liquid medication into a fine mist, allowing easy inhalation for individuals with respiratory issues. It consists of key components: a compressor that generates airflow, tubing connecting the compressor to the nebuliser cup, and either a mask or mouthpiece for inhalation.
By delivering medication directly to the lungs, nebulisers ensure that medication reaches deep into the airways, providing quick relief and improving overall respiratory health.
How Does a Nebuliser Work?
Nebulisers function by transforming liquid medication into a mist that can be inhaled directly into the lungs. The device uses a compressor that generates air pressure, which forces the medication through a small opening, creating fine droplets.
Patients inhale the mist through a mask or mouthpiece, ensuring that the medication penetrates deep into the lungs for maximum effectiveness. Various types of nebulisers, including jet, ultrasonic, and mesh, utilise different technologies to produce the mist.
This continuous flow of medication is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, as it allows for steady dosing and effective symptom management during acute situations.
Why and When Should You Use a Nebuliser?
For most individuals with asthma or COPD, a blue reliever inhaler with a spacer is a practical and effective option for managing flare-ups. This approach is typically as efficient as a nebuliser and is easier to handle. However, certain lung conditions, such as bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis, may require nebulisers at home to manage specific symptoms.
-
Severe Asthma: Nebulisers may be needed at home for high-risk patients or those with difficulty using inhalers due to other health issues.
-
COPD: Generally managed with inhalers, but a nebuliser may be used in severe cases, especially in hospital settings or occasionally at home under medical advice.
-
Bronchiectasis: Nebulisers with saline solutions or antibiotics can help with phlegm build-up and infections.
-
Cystic Fibrosis: Nebulisers are used to deliver medications that manage mucus accumulation and alleviate symptoms.
-
Pulmonary Fibrosis: Nebulisers can assist in phlegm management, though inhalers remain the primary treatment.
In asthma cases, nebulisers are mostly used in emergency settings. If continued at home, a discharge plan will guide the transition back to using inhalers.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Nebuliser?
Based on current guidelines, the benefits of using a nebuliser are specific to certain cases and patient needs:
-
Alternative for patients who struggle with inhalers: Nebulisers are useful for individuals who cannot use inhalers effectively, such as young children, elderly patients, or those with severe coordination or respiratory issues. For these patients, nebulisers provide a reliable method of delivering medication.
-
Support during severe respiratory distress: In emergency settings, such as during a severe asthma attack, nebulisers can allow for slow, deep inhalation without requiring precise coordination, which can offer relief in acute situations. This is why nebulisers are often used in hospitals and ambulance settings.
-
Management of specific conditions: Nebulisers play a role in treating conditions that involve significant mucus build-up, like cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis. In these cases, nebulisers can deliver saline solutions to help thin mucus or administer antibiotics for infections.
-
Controlled medication dosage: Nebulisers ensure a consistent, measured dose of medication over a set duration, which can be beneficial for patients needing precise delivery.
-
Home use for select conditions: In specific cases, such as advanced COPD or severe asthma where other treatments are insufficient, nebulisers may be recommended for home use under a healthcare provider’s guidance.
What Is a Nebuliser Used For?
Nebulisers are designed to treat various respiratory conditions by delivering medication directly to the lungs in a fine mist, allowing for effective absorption. Common conditions treated with nebulisers include:
-
Asthma
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
-
Cystic Fibrosis
-
Bronchiectasis
-
Pulmonary fibrosis
-
Pneumonia
-
Severe croup
Nebulisers can be used for both acute episodes and the ongoing management of chronic respiratory conditions. In acute situations, such as life-threatening asthma attacks, they provide rapid medication delivery for immediate symptom relief. For long-term management , they can help maintain stable breathing and achieve good symptom control.
Typical medications administered via nebulisers include:
-
Bronchodilators (salbutamol & ipratropium): Open airways for easier breathing.
-
Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation in the lungs.
-
Mucolytics (including saline solutions): Thin mucus for easier clearance.
-
Antibiotics: In management of conditions like bronchiectasis to manage secondary bacterial infections
-
Adrenaline: In severe croup cases
For those who need immediate treatment or struggle with using inhalers, nebulisers provide quick, effective relief, supporting optimal respiratory health during acute and ongoing care.
What Are the Different Types of Nebulisers?
Jet
Jet nebulisers are the most common type, using compressed air to create a mist for inhalation. They are cost-effective and reliable, making them suitable for regular treatments. While effective, they can be noisy and bulky, which may inconvenience some users. Jet nebulisers are ideal for chronic conditions, accommodating various medications for effective symptom relief.
Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic nebulisers use high-frequency sound waves to produce a quieter mist, allowing for efficient medication delivery. They are beneficial for rapid relief in acute situations but may not work with all medications, particularly suspensions. Patients should consult their healthcare provider to ensure compatibility.
Mesh
Mesh nebulisers use a vibrating mesh to push liquid through tiny holes, creating a fine mist for easy inhalation. They are portable and quiet, making them convenient for on-the-go use. However, they tend to be more expensive, so patients should consider their needs and budget when choosing a nebuliser.
How Do You Choose the Right Nebuliser?
Choosing the right nebuliser is essential for effective treatment and you should consider individual needs, such as age, condition severity, and how often the device will be used. It is best to compare the different types of nebulisers available such as jet, ultrasonic, and mesh; understanding their specific advantages and disadvantages in various situations.
It's crucial to select a nebuliser that is compatible with prescribed medications, as not all devices work with every type of medication. Additionally, budget constraints and lifestyle factors play a significant role in making the best choice. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide valuable guidance to ensure the right nebuliser is selected for optimal treatment.
How to Use and Maintain Your Nebuliser?
Tips for Using Your Nebuliser
By following these tips, you can improve the effectiveness of your nebuliser therapy and support better respiratory health:
-
Set up the nebuliser according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
-
Measure the prescribed medication and place it in the nebuliser cup.
-
Secure the mask or mouthpiece in place.
-
Turn on the device and inhale slowly until the medication is fully delivered.
-
Sit comfortably and avoid distractions during the treatment.
-
Always wash your hands beforehand to prevent contamination.
How to Clean Your Nebuliser
To maintain the effectiveness of your nebuliser and prevent contamination, it’s important to follow a regular cleaning routine:
-
Daily cleaning involves rinsing the mask or mouthpiece and washing the nebuliser cup with warm, soapy water right after use.
-
For a more thorough cleaning, perform a deep clean weekly by soaking all parts in a vinegar-water solution (one part vinegar to three parts water) for about 30 minutes.
-
After soaking, rinse each component under warm running water to remove any vinegar residue. Allow all parts to air dry completely on a clean towel before storing them.
-
Proper storage is essential; keep the nebuliser parts in a dry, dust-free environment to ensure they are ready for the next use.
Nebuliser vs. Inhaler vs. Spacer: What’s the Difference?
What Is an Inhaler?
An inhaler is a portable device used to deliver quick doses of medication during asthma attacks. While inhalers are convenient for on-the-go relief, nebulisers may be more effective for severe cases or for those who struggle with coordination. Inhalers are preferred for travel or when immediate relief is needed, as they are compact and easy to use.
What Is a Spacer?
A spacer is an attachment for inhalers that enhances medication delivery by allowing for better timing and inhalation. It holds the medication mist longer, making it easier for individuals to inhale the medicine effectively. While spacers assist with inhalers, nebulisers are typically used for more serious conditions requiring longer treatment times.
|
|
|
|
|
Inhaler Image from Asthma & Lung UK |
Spacer Image from National Asthma Council Australia |
Nebuliser Image from National Asthma Council Australia |
Why Doesn’t a Nebuliser Work for Everyone?
A nebuliser might not work for everyone due to incorrect usage, insufficient dosage, or the patient's condition not responding well to nebulised treatments. Factors such as age and health status can influence effectiveness. If a nebuliser isn't effective, consult a healthcare provider for alternative options like inhalers or spacers.
What Are the Side Effects of a Nebuliser?
Using a nebuliser can lead to several side effects, including:
-
Throat Irritation: Commonly experienced due to the medication or mist.
-
Dry mouth: Often occurs after treatment sessions.
-
Hoarseness: Can result from the delivery method or specific drugs.
While most side effects are mild, some medications may cause serious reactions. Rarely, users may experience severe allergic reactions requiring immediate medical attention.
To minimise side effects, consider these tips:
-
Stay hydrated: Drink water before and after use.
-
Rinse your mouth: Helps remove lingering medication and reduces irritation.
References:
-
Australian asthma handbook. Australian Asthma Handbook. https://www.asthmahandbook.org.au/
-
The National Asthma Council Australia. National Asthma Council Australia. https://www.nationalasthma.org.au/
-
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care. (2022, November 15). National asthma strategy 2018. https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/national-asthma-strategy-2018?language=en
-
The Royal Children’s hospital melbourne. The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne. (n.d.). https://www.rch.org.au/be-positive/A_childs_guide_to_hospital/Nebulisers/
-
Department of Health & Human Services. (1999, October 25). Asthma management. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/asthma-management